本文共 7951 字,大约阅读时间需要 26 分钟。
Summary: this tutorial introduces you to C pointer, which is an important concept in C programming language. Pointers give you a flexible and powerful way of manipulating data in your programs.
Introduction to C Pointer
When you define a in your program, the compiler allocates a memory location with a unique address to store that variable’s value. You then access the memory address through the variable name.
For example, when you define a variable:
You specified variable name ( x ), its data type int and its value, 10. The variable x resides in the memory with a unique memory address. To get the memory address of the variable x, you use unary operator & as follows:
In our system, the memory address of x is:
Because memory address of x is a number ( 28FF1C), you can use another variable to store it e.g., px as the following picture:
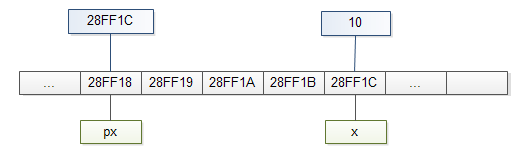
In C, we say that px points to x, or px is a pointer to x.
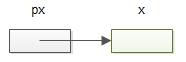
By definition, C pointer is a special variable that holds the memory address of another variable.
There is a special kind of pointer called that holds a memory address of a . Check it out the for more information.
Declaring a pointer
Like a variable, before using a pointer, you have to declare it. The following illustrates the syntax of declaring a pointer:
First, you specify the data type of the variable that the pointer point to. The type can be any valid such as int, char, float or even void.
Second, you place the indirection operator ( *) in front of the pointer name to indicate that this is a pointer that points to a variable with a specific type e.g. int, not a variable of the type int
Third, you provide the name for the pointer. The name of pointers must follow the naming rules of . By convention, in C, pointer name begins with p to help distinguish between a pointer and a variable in your programs.
The following example defines 2 pointers that point to int variables, an a pointer that points to a char variable.
Initializing Pointers
If you declare a pointer without initializing it, you have an uninitialized pointer. With an uninitialized pointer, you cannot do anything with it.
To initialize a pointer, you assign the memory address of another variable to the pointer using the address-of operator ( &) as follows:
For example, to assign the address of the x variable to the px pointer you use the following syntax:
Using pointers
After initializing a pointer, you can manipulate the variable which the pointer points to using the indirection operator ( *).
For example, we can display the value of x through the px pointer as follows:
We can change the value of x through the px pointer as well:
In C, accessing the value of a variable through the variable name is called direct access, and accessing the value of a variable through a pointer that points to the variable is known as indirect access or indirection.
Putting it all together.
The following is the output of the program:
Pointer & Array
Basically any operation on an , which can be done using array subscript, can be achieved through a pointer to the array.
Let’s take a look at an example.
This declares an array of 10 integers. Underneath, there is a block of memory with 10 consecutive objects defining as follows:
![]()
The a[i] refers the ith element of the a array. The following defines a pointer that points to the first element of the a array:
Because the pa pointer points to the first element of the a array, *pa is the value of the first element. And (pa+1) points to the next element of the array, and (pa+i) points to the ith element.
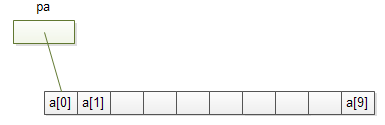
Recall that the name of an array is the memory address of the first element, therefore the following assignment:
can be rewritten as follows:
After assigning the pointer to the first element of an array, you can perform any operations on that array. The following example illustrates how to manipulate an array via a pointer.
In this tutorial, you have learned about C pointer, which is a special variable that store memory address of another variable. You also learned the relationship between a pointer and an array, and how to manipulate an array through a pointer.
转载自:http://www.zentut.com/c-tutorial/c-pointer/